Blood
Blood is a connective tissue. Its function is transport of gases, nutrients, waste products, hormones and enzymes. It regulates the PH and osmosis. It maintain body temperature and provide protection against foreign substances.
Composition of blood
It is composed of plasma and other formed elements. Plasma is 55% of blood and other elements are 45%.
Plasma
Plasma is composed of 7% proteins, 91% water and 2% other solutes. Proteins include albumen (58%), globulin (38%), fibrinogen (4%). Other solutes include nutrients, ions, waste products, gases, and regulatory substances.
Formed elements
They include white blood cells (5-9thousands), red blood cell (4.2-6.2 million) and platelets (250-400thousands). White blood cells include neutrophils (60-70%), lymphocytes (20-25%), monocytes (3-8%), eosinophils (2-4%) and basophils (0.5-1%).
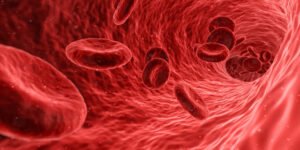
Hematopoiesis
it is a process of blood cell production. In fetus and embryo, this process occurs in tissues such as thymus, liver, spleen yolk sac, red bone marrow and lymph node. After birth, this process is mainly confined to red bone marrow and some lymphatic tissue. The red bone marrow is located into the vertebrae, sternum, proximal femur, ribs and proximal humerus of adult.
All the formed elements are obtained from population of the stem cells called hemocytoblasts. When hemocytoblasts divide, one daughter cell will remain a hemocytoblast while second one differentiates to form one of two types of intermediate stem cells, myeloid stem cell or lymphoid stem cell. The myeloid stem cell will give rise to RBCs, platelets and most of WBCs.
The myeloid cell can differentiate into the following types of cells:
- Proerythroblasts: which will develop into red blood cells
- Myeloblasts: which will develop into basophils, neutrophils, eosinophils.
- Monoblasts: they will develop into monocytes.
- Megakaryoblasts: they will develop into platelets:
The lymphoid stem cell will give rise to lymphocytes.
The regulation of the development of different types of formed elements is done by chemical signals like colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) control WBCs and RBCs production is controlled by Erythropoietin hormone.
The red blood cells (RBCs), the white blood cells(WBCs) and the platelets
1: Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
RBCs are almost seven hundred times more numerous than white blood cells and seventeen times more numerous than platelets in blood. In males, about 5.4 million red blood cells per microliter of blood is present. The range is 4.6- 6.2 million. While in females, about 4.8 million per micro liter are present (range 4.2-5.4 million). An average adult contains twenty-five trillion red blood cells. They do not move at their own will but the forces which cause the blood to circulate passively transported them.
Structure and advantages
They are biconcave discs and are 7.5 micrometers in diameter. They are anucleate. Their surface area increased as compared to discs.
- The large surface area lets the gases move into and out of red blood cells more rapidly.
- The RBCs fold or flex around its thin centre to decrease its size which will enable it to pass easily through smaller blood vessels.
-
red blood cells
2: White Blood Cells (WBCs)
They are also known as leukocytes. They protect the body against microorganisms and eliminate dead cells and debris.
Movements
1: Ameboid:
Some have ameboid movement (the movement of cytoplasmic extension).
2: Diapedesis:
In this movement, they become thin, increase in length, and then slip through or between the cells of the blood vessel wall.
3: Chemotaxis:
The movement toward external material and dead cells inside tissues.
There are five types of white blood cells, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes and lymphocytes.
3: Platelets
They are the cell fragments squeezed out from megakaryocytes in red bone marrow. They are disc shaped and are about 3 micrometers in diameter. The proteins and glycoproteins on their surface allow them to attach to other molecules like collagen in connective tissue. These attachments play important role in preventing the blood loss. The cytoplasm of platelets contains actin and myosin which can cause platelets contraction. 5-9 days are the life expectancy of platelets.
Platelets play a crucial role in preventing blood loss by following ways,
By platelets plug formation which seals the holes in small vessels
By promoting the contraction and formation of clots that aid in sealing off larger wounds in the vessels.